Deciphering the Anatomy of a Laptop: A Comprehensive Guide to Laptop Parts
Discover the inner workings of laptops in our comprehensive guide, "Deciphering the Anatomy of a Laptop: A Comprehensive Guide to Laptop Parts." From CPUs and GPUs to storage devices and input devices, explore each component's function and significance. Whether you're a casual user, professional, or gaming enthusiast, delve into the intricate world of laptop parts to make informed decisions about your computing needs.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)

In the digital age, laptops have become an indispensable tool for work, education, and entertainment. These portable computing devices pack a myriad of components that work seamlessly together to deliver functionality and performance. Understanding the intricate anatomy of a laptop is not only intriguing but also essential for users to make informed decisions when purchasing, upgrading, or troubleshooting their devices.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate world of laptop parts. From the central processing unit (CPU) to the smallest screws holding the chassis together, we'll explore each component's function, significance, and how they contribute to the overall functionality of a laptop.
So, grab your magnifying glass and let's embark on an illuminating journey into the inner workings of laptops.
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
At the heart of every laptop lies the central processing unit (CPU). Often referred to as the brain of the computer, the CPU executes instructions, performs calculations, and manages data flow. In essence, it's responsible for carrying out all the tasks assigned by the user and software applications.
Modern laptops feature CPUs manufactured by companies like Intel and AMD. These processors come in various configurations, including dual-core, quad-core, and even octa-core designs, each offering different levels of performance and power efficiency.
The CPU's clock speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), determines how quickly it can process instructions. Higher clock speeds typically result in faster performance, making the laptop more responsive during tasks such as multitasking, gaming, or video editing.
2. Random Access Memory (RAM)
While the CPU handles the actual computation, the random access memory (RAM) serves as temporary storage for data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly. Think of RAM as a workspace where the CPU can store and retrieve information rapidly, significantly speeding up system performance.
Laptops come with varying amounts of RAM, typically ranging from 4GB to 32GB or more. The amount of RAM directly impacts the laptop's ability to multitask efficiently. More RAM allows you to run multiple applications simultaneously without experiencing significant slowdowns or lag.
Additionally, the type and speed of RAM, such as DDR3 or DDR4, influence overall system performance. Upgrading RAM is one of the most common and effective ways to boost a laptop's speed and responsiveness.
3. Storage Devices
Storage devices play a crucial role in storing data, applications, and the operating system on a laptop. Traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) have long been the standard storage solution, offering large capacities at relatively low costs. However, solid-state drives (SSDs) have gained popularity due to their superior speed and reliability.
SSDs utilize flash memory to store data, resulting in significantly faster read and write speeds compared to HDDs. This translates to quicker boot times, faster application launches, and snappier overall system responsiveness.
Hybrid storage solutions, which combine the capacity of an HDD with the speed of an SSD, offer a compromise between storage space and performance. Many modern laptops feature SSDs as the primary storage device for improved performance, with HDDs used for additional storage capacity.
4. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
The graphics processing unit (GPU) is responsible for rendering images, videos, and animations on the laptop's display. While integrated graphics processors (iGPUs) built into the CPU handle basic graphical tasks, dedicated GPUs offer significantly higher performance for demanding tasks such as gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering.
NVIDIA and AMD are the primary manufacturers of dedicated laptop GPUs, offering a range of models catering to different performance levels and price points. High-end gaming laptops often feature powerful discrete GPUs with dedicated video memory, enabling smooth gameplay at high resolutions and frame rates.
For professionals working with graphic-intensive applications such as Adobe Creative Suite or AutoCAD, a robust GPU is essential for achieving optimal performance and productivity.
5. Display Panel
The display panel is the window to the digital world, allowing users to interact with their laptops visually. Laptops come in various screen sizes, ranging from compact 11-inch displays to expansive 17-inch panels, catering to different usage preferences and mobility needs.
The quality of the display panel is determined by factors such as resolution, color accuracy, brightness, and refresh rate. Higher-resolution displays offer sharper images and text, making them ideal for tasks such as photo editing and graphic design.
Additionally, features like high dynamic range (HDR) support and wide color gamut coverage enhance the visual experience, especially when consuming multimedia content or playing games.
6. Input Devices
Input devices such as the keyboard and touchpad are the primary means of interacting with a laptop. Keyboards come in various layouts and designs, including traditional membrane keyboards and more tactile mechanical keyboards favored by gamers and typing enthusiasts.
The touchpad, or trackpad, serves as a substitute for a mouse, allowing users to navigate the cursor and perform gestures such as scrolling and pinch-to-zoom. Many laptops also support touchscreen input, providing a more intuitive and versatile user experience, especially in tablet or convertible form factors.
7. Battery
The battery is what enables laptops to remain portable and independent of external power sources. Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type found in laptops, offering a balance between energy density, weight, and lifespan.
Battery life varies depending on factors such as usage patterns, screen brightness, and system configuration. Manufacturers often provide estimated battery life figures based on standardized tests, but real-world usage may differ significantly.
Efforts to improve battery life include optimizing hardware and software efficiency, as well as implementing power-saving features such as low-power modes and dynamic voltage scaling.
8. Chassis and Cooling System
The chassis serves as the structural framework of the laptop, housing and protecting its internal components. Laptop chassis come in various materials, including plastic, aluminum, and magnesium alloys, each offering different levels of durability, weight, and aesthetics.
The cooling system is responsible for dissipating heat generated by the laptop's components, particularly the CPU and GPU. Most laptops use a combination of heat pipes, heat sinks, and fans to regulate temperatures and prevent overheating.
Thermal management is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing thermal throttling, where the CPU or GPU reduces clock speeds to avoid excessive heat buildup.
Laptops are marvels of modern engineering, packing a myriad of components into sleek and portable form factors. From the powerful CPU and GPU to the vibrant display and ergonomic input devices, every part plays a vital role in delivering a seamless computing experience.
Understanding the anatomy of a laptop not only enhances appreciation for the technology but also empowers users to make informed decisions when selecting, upgrading, or troubleshooting their devices. Whether you're a casual user, professional, or gaming enthusiast, delving into the world of laptop parts opens doors to endless possibilities and optimizations for your computing needs.
Types of Laptop Parts
Laptops are intricate devices composed of various parts that work together to deliver functionality and performance. Here are the types of laptop parts commonly found in these portable computing devices:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Often referred to as the brain of the computer, the CPU executes instructions, performs calculations, and manages data flow.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): RAM serves as temporary storage for data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly, enhancing system performance during multitasking.
- Storage Devices: These include traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs), which store data, applications, and the operating system.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Responsible for rendering images, videos, and animations on the laptop's display, GPUs come in integrated and dedicated forms, catering to different performance needs.
- Display Panel: The display panel provides the visual interface for interacting with the laptop, with factors like resolution, color accuracy, and refresh rate influencing the viewing experience.
- Input Devices: Keyboards, touchpads, and touchscreens serve as primary input methods, allowing users to interact with the laptop and navigate the interface.
- Battery: Lithium-ion batteries power laptops, enabling them to operate independently of external power sources for extended periods.
- Chassis and Cooling System: The chassis provides structural support and protection for internal components, while the cooling system regulates temperatures to prevent overheating.
Understanding the different types of laptop parts is essential for users to make informed decisions when purchasing, upgrading, or troubleshooting their devices. Each component plays a crucial role in shaping the overall functionality and performance of a laptop.
Benefits of Laptop Parts
Laptop parts play a vital role in the overall functionality and performance of these portable computing devices. Here are some key benefits of various laptop parts:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU):
- Efficient Execution: The CPU executes instructions and performs calculations, enabling smooth operation of software applications and tasks.
- Multitasking Capability: A powerful CPU allows for seamless multitasking, enabling users to run multiple programs simultaneously without experiencing significant slowdowns.
- Random Access Memory (RAM):
- Improved Performance: RAM serves as temporary storage for data and instructions, facilitating faster access to frequently used information and enhancing system responsiveness.
- Enhanced Multitasking: Higher RAM capacities enable smoother multitasking, allowing users to switch between applications seamlessly without experiencing lag.
- Storage Devices:
- Faster Data Access: Solid-state drives (SSDs) offer faster read and write speeds compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), resulting in quicker boot times and faster application launches.
- Reliability: SSDs have no moving parts, making them more resistant to physical shock and less prone to mechanical failure than HDDs, ensuring data integrity and reliability.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU):
- Enhanced Visual Experience: Dedicated GPUs deliver smoother graphics rendering and improved frame rates, providing an immersive visual experience for gaming, video editing, and graphic design.
- Increased Productivity: A powerful GPU accelerates rendering and processing tasks, reducing wait times and improving productivity for professionals working with graphic-intensive applications.
- Display Panel:
- Crisp Visuals: High-resolution displays with vibrant colors and wide viewing angles offer an immersive visual experience, enhancing productivity and enjoyment when working or consuming multimedia content.
- Versatility: Touchscreen displays provide intuitive input options, enabling users to interact with the laptop using gestures and stylus input, ideal for creative tasks and presentations.
- Input Devices:
- Comfortable Typing: Ergonomically designed keyboards with tactile feedback and responsive keys ensure comfortable typing experiences, reducing fatigue during extended use.
- Precise Navigation: Responsive touchpads and accurate pointing devices facilitate precise cursor control and smooth navigation, enhancing user productivity and efficiency.
- Battery:
- Portability: Long-lasting battery life enables users to work, study, or entertain themselves on the go, without the need for constant access to a power source.
- Convenience: Battery-powered operation provides flexibility and convenience, allowing users to use their laptops in various environments, whether at home, in the office, or outdoors.
- Chassis and Cooling System:
- Durability: Sturdy chassis materials and robust construction protect internal components from physical damage, ensuring long-term durability and reliability.
- Thermal Management: Efficient cooling systems prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance levels, prolonging the lifespan of the laptop and preventing thermal throttling.
Overall, each laptop part contributes to the overall user experience by enhancing performance, reliability, and versatility, making laptops indispensable tools for work, entertainment, and creativity.
Functions of Laptop Parts
Laptop parts are integral components that work together to facilitate various functions and operations of these portable computing devices. Here's a breakdown of the functions of key laptop parts:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU):
- Executes Instructions: The CPU carries out instructions provided by software programs, performing calculations, data processing, and logic operations.
- Manages Resources: It coordinates the activities of other hardware components, allocating resources such as memory, input/output devices, and processing power as needed.
- Controls System Clock: The CPU generates clock signals that synchronize the timing of operations within the computer system, ensuring proper coordination and execution of tasks.
- Random Access Memory (RAM):
- Stores Data Temporarily: RAM serves as temporary storage for data and program instructions that are actively being used by the CPU.
- Facilitates Quick Access: It allows the CPU to access data rapidly, significantly speeding up system performance by reducing the need to retrieve information from slower storage devices.
- Supports Multitasking: RAM enables the simultaneous execution of multiple tasks and programs, providing a seamless user experience without significant slowdowns or delays.
- Storage Devices:
- Stores Data Permanently: Hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) store data and files, including the operating system, software applications, documents, and multimedia content.
- Enables Data Retrieval: Storage devices allow users to access stored data for reading, writing, and modification, providing long-term data retention and accessibility.
- Facilitates System Boot-Up: The operating system and essential system files are stored on storage devices, allowing the laptop to boot up and initialize its components during the startup process.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU):
- Renders Graphics: The GPU is responsible for processing and rendering visual elements such as images, videos, and 3D graphics on the laptop's display.
- Accelerates Graphics Performance: Dedicated GPUs offload graphical processing tasks from the CPU, enhancing performance in tasks such as gaming, video editing, and graphic design.
- Supports Display Output: GPUs drive the display output, generating signals that are sent to the laptop's screen to produce images and visuals for the user to see.
- Display Panel:
- Displays Visual Output: The display panel presents visual information to the user, including text, images, videos, and graphical user interfaces.
- Provides User Interface: The display serves as the primary interface for interacting with the laptop, allowing users to view and interact with software applications, files, and content.
- Supports User Interaction: Touchscreen displays enable direct interaction through touch gestures, allowing users to navigate, select, and manipulate on-screen elements using their fingers or stylus.
- Input Devices:
- Facilitates User Input: Input devices such as keyboards, touchpads, and pointing devices enable users to input commands, text, and gestures into the laptop.
- Controls Cursor Movement: Pointing devices and touchpads control the movement of the cursor on the screen, allowing users to navigate graphical user interfaces and interact with on-screen elements.
- Enables Text Entry: Keyboards provide a means for users to input text and commands into the laptop, facilitating communication, data entry, and text-based tasks.
- Battery:
- Provides Power Supply: The battery supplies electrical power to the laptop, allowing it to operate independently of external power sources for a certain duration.
- Supports Portability: Batteries enable laptops to be used in various locations and environments without the need for constant access to electrical outlets, enhancing portability and mobility.
- Maintains System Operation: During power outages or when disconnected from power sources, batteries ensure continuous operation of the laptop, allowing users to save their work and shut down the system gracefully.
- Chassis and Cooling System:
- Provides Structural Support: The chassis houses and protects internal components, providing a sturdy framework for the laptop and ensuring durability and structural integrity.
- Dissipates Heat: The cooling system regulates the temperature of internal components by dissipating heat generated during operation, preventing overheating and maintaining optimal performance.
- Enhances Ergonomics: The design of the chassis and cooling system contributes to the overall ergonomics and usability of the laptop, providing comfort and convenience for users during operation.
Each laptop part performs specific functions that collectively contribute to the overall operation, performance, and user experience of the device. Understanding the roles of these components is essential for users to appreciate the complexity and functionality of laptops and to make informed decisions regarding usage, maintenance, and upgrades.
Features of Laptop Parts
Laptop parts encompass a wide array of features, each contributing to the overall functionality and performance of these portable computing devices. Here's a breakdown of the key features of laptop parts:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU):
- Clock Speed: The CPU's clock speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), determines how quickly it can execute instructions and process data.
- Core Count: CPUs come with varying numbers of cores, with more cores enabling the processor to handle multiple tasks simultaneously.
- Cache Size: CPU cache stores frequently accessed data and instructions, reducing the time it takes for the CPU to retrieve information.
- Random Access Memory (RAM):
- Capacity: RAM capacity, measured in gigabytes (GB), determines how much data the laptop can store temporarily for quick access by the CPU.
- Speed: RAM speed, measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz), influences the rate at which data can be transferred between the RAM modules and the CPU.
- Storage Devices:
- Type: Storage devices can be traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs), each offering different performance characteristics and storage capacities.
- Capacity: Storage capacity refers to the amount of data that can be stored on the device, ranging from gigabytes (GB) to terabytes (TB) for HDDs and SSDs.
- Read/Write Speed: SSDs typically offer faster read and write speeds compared to HDDs, resulting in quicker data access and file transfers.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU):
- Model: GPUs come in various models and architectures from manufacturers like NVIDIA and AMD, offering different levels of performance and features.
- Dedicated Memory: Dedicated GPUs have their own dedicated video memory (VRAM), which stores graphical data and textures for faster access by the GPU.
- CUDA Cores / Stream Processors: The number of CUDA cores (NVIDIA) or stream processors (AMD) determines the GPU's parallel processing capabilities.
- Display Panel:
- Resolution: Display resolution refers to the number of pixels on the screen, with higher resolutions offering sharper and more detailed images.
- Panel Type: Display panels can be LCD, LED, OLED, or IPS, each with its own characteristics such as color accuracy, viewing angles, and response times.
- Refresh Rate: Refresh rate measures how many times the display updates per second, with higher refresh rates resulting in smoother motion and reduced motion blur.
- Input Devices:
- Keyboard Type: Keyboards can be membrane, scissor-switch, or mechanical, offering different levels of tactile feedback and typing comfort.
- Touchpad Features: Touchpads may support multitouch gestures, palm rejection, and customizable settings for enhanced usability and navigation.
- Touchscreen Capability: Some laptops feature touchscreen displays, allowing users to interact directly with on-screen elements using touch gestures.
- Battery:
- Capacity: Battery capacity, measured in watt-hours (Wh), determines how much energy the battery can store and how long the laptop can operate on a single charge.
- Battery Life: Battery life refers to the duration the laptop can run on battery power before needing to be recharged, influenced by factors such as usage patterns and power-saving settings.
- Chassis and Cooling System:
- Material: Laptop chassis can be made of plastic, aluminum, magnesium alloy, or carbon fiber, each offering different levels of durability, weight, and aesthetics.
- Cooling Mechanism: Cooling systems may include heat pipes, heat sinks, and fans to dissipate heat generated by internal components and maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Understanding the features of laptop parts is essential for users to assess performance, functionality, and suitability for their computing needs. Whether for work, gaming, or multimedia consumption, choosing the right laptop parts ensures a satisfying and efficient user experience.
Recent Advancements in Laptop Parts
Recent advancements in laptop parts have pushed the boundaries of performance, efficiency, and user experience. Here are some notable developments across various laptop components:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU):
- Higher Core Counts: Manufacturers like Intel and AMD have introduced CPUs with higher core counts, offering increased multitasking capabilities and improved performance for demanding tasks such as gaming, content creation, and data processing.
- Improved Power Efficiency: Advancements in CPU architecture and manufacturing processes have led to more power-efficient designs, resulting in longer battery life and reduced heat generation in laptops.
- Random Access Memory (RAM):
- Higher Speeds and Capacities: DDR5 RAM technology has started to make its way into laptops, offering faster data transfer speeds and higher capacities compared to DDR4. This allows for smoother multitasking and improved overall system performance.
- Low-power Variants: Manufacturers are developing low-power variants of RAM modules, optimized for energy efficiency and extending battery life in laptops without compromising performance.
- Storage Devices:
- PCIe 4.0 SSDs: PCIe 4.0 SSDs provide significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to previous generations, reducing loading times and improving overall system responsiveness in laptops.
- QLC NAND Flash: Quad-level cell (QLC) NAND flash technology has enabled higher storage densities in SSDs, allowing for larger capacities without a significant increase in cost or physical size.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU):
- Ray Tracing Support: Recent GPU architectures from NVIDIA and AMD feature hardware-accelerated ray tracing capabilities, delivering realistic lighting and reflections in games and other graphical applications on laptops.
- AI-based Features: GPUs with dedicated AI processing units offer features such as AI-enhanced upscaling, real-time noise reduction, and content-aware video editing, improving visual quality and productivity on laptops.
- Display Panel:
- High Refresh Rate Displays: Laptops with high refresh rate displays, often exceeding 120Hz or 144Hz, provide smoother motion and reduced motion blur, enhancing gaming and multimedia experiences.
- HDR Support: HDR-capable displays offer improved contrast, color accuracy, and brightness, delivering more vibrant and lifelike visuals in movies, games, and other HDR content on laptops.
- Input Devices:
- Enhanced Keyboards: Keyboards with improved key switches, customizable RGB lighting, and advanced anti-ghosting technology provide a more tactile and responsive typing experience on gaming and productivity laptops.
- Precision Touchpads: Precision touchpads with larger surface areas, multitouch gestures, and palm rejection technology offer smoother and more intuitive navigation on laptops running Windows 10 or later.
- Battery:
- Fast Charging: Laptops equipped with fast-charging technology can recharge their batteries to a significant percentage in a short amount of time, providing users with more flexibility and convenience in their daily usage.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: Advances in battery chemistry and power management algorithms have resulted in more energy-efficient laptops, extending battery life and reducing environmental impact.
- Chassis and Cooling System:
- Thinner and Lighter Designs: Manufacturers are incorporating innovative materials and engineering techniques to create thinner and lighter laptop chassis without compromising durability or thermal performance.
- Advanced Cooling Solutions: Laptops feature advanced cooling solutions such as vapor chamber cooling, liquid metal thermal interfaces, and multi-fan configurations to dissipate heat effectively and maintain optimal performance during intensive tasks.
These recent advancements in laptop parts collectively contribute to delivering a more immersive, efficient, and satisfying computing experience for users across various usage scenarios. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further innovations that will further enhance the capabilities and versatility of laptops in the future.
Future Trends in Laptop Parts
Anticipating future trends in laptop parts requires considering emerging technologies and evolving consumer needs. Here are some potential future trends in laptop parts:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU):
- AI Integration: CPUs with dedicated AI processing units may become commonplace, enabling AI-powered features such as real-time language translation, intelligent image recognition, and personalized user experiences.
- Quantum Computing: While still in the experimental stage, advancements in quantum computing may eventually lead to CPUs with quantum processors, offering unparalleled processing power and capabilities for complex calculations and simulations.
- Random Access Memory (RAM):
- DDR5 Adoption: DDR5 RAM is expected to become the standard in future laptops, offering higher speeds, increased capacities, and improved energy efficiency compared to DDR4, further enhancing system performance and multitasking capabilities.
- Non-Volatile RAM (NVRAM): Non-volatile RAM technologies such as MRAM (Magnetoresistive RAM) and FeRAM (Ferroelectric RAM) may gain traction, providing faster access times and data persistence without the need for constant power.
- Storage Devices:
- NVMe Over Fabrics (NVMe-oF): NVMe-oF technology could enable laptops to access remote storage devices over high-speed networks with low latency, allowing for seamless integration of cloud storage and centralized data management.
- Storage Class Memory (SCM): SCM, such as Intel Optane Memory, could become more prevalent in laptops, bridging the performance gap between RAM and storage by offering high-speed, non-volatile memory for caching and storage acceleration.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU):
- Ray Tracing Optimization: GPUs optimized for ray tracing may become more efficient and affordable, enabling realistic lighting and reflections in games and other graphical applications on a wider range of laptops.
- Integrated AI Acceleration: GPUs with integrated AI processing units may become standard, enabling on-device AI inference for tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and augmented reality applications.
- Display Panel:
- Foldable and Rollable Displays: Flexible display technologies may lead to the development of laptops with foldable or rollable screens, offering versatile form factors and enhanced portability without compromising screen size or resolution.
- MicroLED Technology: MicroLED displays could become more prevalent in laptops, offering superior brightness, contrast, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD and OLED panels.
- Input Devices:
- Gesture Recognition: Advanced camera and sensor technologies may enable laptops to recognize and interpret hand gestures for intuitive user interaction, enhancing productivity and convenience in touchless computing environments.
- Haptic Feedback Keyboards: Keyboards with haptic feedback mechanisms could provide tactile sensations and feedback, simulating the feel of physical keys while typing on flat touch surfaces.
- Battery:
- Solid-State Batteries: Solid-state battery technology may replace traditional lithium-ion batteries in laptops, offering higher energy densities, faster charging times, and improved safety.
- Wireless Charging: Laptops with built-in wireless charging capabilities may become more prevalent, allowing users to recharge their devices conveniently without the need for cables or docking stations.
- Chassis and Cooling System:
- Advanced Thermal Solutions: Innovations in cooling technology, such as graphene-based thermal materials and miniature vapor chamber cooling systems, could improve heat dissipation and thermal management in laptops, enabling higher performance and thinner designs.
- Eco-friendly Materials: Manufacturers may prioritize the use of sustainable and recyclable materials in laptop chassis construction, reducing environmental impact and promoting eco-conscious design practices.
These future trends in laptop parts are driven by advancements in semiconductor technology, materials science, and user experience design, paving the way for more powerful, efficient, and versatile computing devices in the years to come.
Recent Advancements in Laptop Parts
Recent advancements in laptop parts have propelled the capabilities of these portable computing devices to new heights. Here are some notable developments across various components:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU):
- Higher Core Counts: Manufacturers like Intel and AMD have introduced CPUs with higher core counts, enabling laptops to handle more simultaneous tasks efficiently.
- Improved Efficiency: Advancements in architecture and manufacturing processes have led to CPUs that deliver better performance while consuming less power, resulting in longer battery life and reduced heat generation.
- Integrated AI Acceleration: Modern CPUs feature integrated AI accelerators, enhancing performance in AI-related tasks such as voice recognition, image processing, and machine learning.
- Random Access Memory (RAM):
- DDR5 Memory: DDR5 RAM technology has started to appear in laptops, offering faster data transfer speeds and higher capacities compared to DDR4, improving overall system performance and multitasking capabilities.
- Low-power Variants: Low-power DDR4 and DDR5 RAM modules are being developed to optimize energy efficiency in laptops, extending battery life without compromising performance.
- LPDDR4X/LPDDR5X: Low-power variants of DDR4 and DDR5 RAM, such as LPDDR4X and LPDDR5X, are becoming more prevalent in laptops, enabling thinner and lighter designs while maintaining high memory bandwidth.
- Storage Devices:
- PCIe 4.0 SSDs: PCIe 4.0 solid-state drives (SSDs) offer significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to previous generations, reducing loading times and improving overall system responsiveness in laptops.
- NVMe Protocol: NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs have become the standard for storage in laptops, providing lower latency and higher throughput compared to traditional SATA SSDs.
- QLC NAND Flash: Quad-level cell (QLC) NAND flash technology has enabled higher storage densities in SSDs, allowing for larger capacities without a significant increase in cost or physical size.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU):
- Ray Tracing Support: GPUs with hardware-accelerated ray tracing capabilities deliver realistic lighting and reflections in games and other graphical applications, enhancing visual fidelity and immersion on laptops.
- DLSS Technology: NVIDIA's Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS) technology uses AI to upscale lower-resolution images in real-time, improving performance and image quality in games on laptops equipped with RTX GPUs.
- Integrated Graphics Improvements: Integrated GPUs from Intel and AMD have seen significant performance improvements, enabling casual gaming and multimedia editing tasks without the need for a dedicated GPU.
- Display Panel:
- High Refresh Rate Displays: Laptops with high refresh rate displays, often exceeding 120Hz or 144Hz, provide smoother motion and reduced motion blur, enhancing gaming and multimedia experiences.
- HDR Support: HDR-capable displays offer improved contrast, color accuracy, and brightness, delivering more vibrant and lifelike visuals in movies, games, and other HDR content on laptops.
- OLED Screens: Laptops with OLED displays have become increasingly popular, offering deeper blacks, higher contrast ratios, and wider color gamuts compared to traditional LCD panels.
- Input Devices:
- Advanced Keyboard Designs: Keyboards with improved key switches, customizable RGB lighting, and anti-ghosting technology provide a more tactile and responsive typing experience on gaming and productivity laptops.
- Precision Touchpads: Precision touchpads with larger surface areas, multitouch gestures, and palm rejection technology offer smoother and more intuitive navigation on laptops running Windows 10 or later.
- Touchscreen Displays: Laptops with touchscreen displays provide versatile input options, enabling touch-based interactions and handwriting recognition for creative and productivity tasks.
- Battery:
- Fast Charging: Laptops with fast-charging technology can recharge their batteries to a significant percentage in a short amount of time, providing users with more flexibility and convenience in their daily usage.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: Advances in battery chemistry and power management algorithms have resulted in more energy-efficient laptops, extending battery life and reducing environmental impact.
- Chassis and Cooling System:
- Thinner and Lighter Designs: Manufacturers are incorporating innovative materials and engineering techniques to create thinner and lighter laptop chassis without compromising durability or thermal performance.
- Advanced Cooling Solutions: Laptops feature advanced cooling solutions such as vapor chamber cooling, liquid metal thermal interfaces, and multi-fan configurations to dissipate heat effectively and maintain optimal performance during intensive tasks.
These recent advancements in laptop parts collectively contribute to delivering a more immersive, efficient, and satisfying computing experience for users across various usage scenarios. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further innovations that will further enhance the capabilities and versatility of laptops in the future.

Positive and Negative Effects on Laptop Parts
Laptop parts are subject to various factors and conditions that can have both positive and negative effects on their performance, durability, and overall functionality. Let's explore some of these effects:
Positive Effects:
- Technological Advancements: Continuous advancements in technology lead to the development of more powerful and efficient laptop parts. Faster processors, higher-capacity RAM, and improved storage devices contribute to better overall performance and user experience.
- Enhanced Productivity: Upgraded laptop parts often result in increased productivity for users. Faster CPUs, larger RAM capacities, and high-speed storage devices enable smoother multitasking, faster data processing, and quicker application launches, allowing users to accomplish tasks more efficiently.
- Improved Gaming Experience: High-performance GPUs and displays with high refresh rates and resolutions enhance the gaming experience on laptops. Gamers can enjoy smoother gameplay, better graphics quality, and reduced input lag, leading to a more immersive gaming experience.
- Enhanced Portability: Advances in battery technology and energy efficiency result in longer battery life and reduced power consumption, improving the portability of laptops. Users can work or entertain themselves on the go without constantly needing to recharge their devices.
- Innovative Form Factors: Technological advancements enable the creation of innovative laptop form factors and designs. Convertible laptops with touchscreen displays, 2-in-1 devices, and ultraportable laptops offer versatility and flexibility to users, catering to diverse usage preferences.
Negative Effects:
- Overheating: Intensive usage or inadequate cooling systems can lead to overheating of laptop parts, which may cause performance degradation, system instability, and even hardware failure. Over time, excessive heat can reduce the lifespan of components such as CPUs, GPUs, and batteries.
- Hardware Compatibility Issues: Upgrading individual laptop parts, such as replacing the CPU or GPU, may lead to compatibility issues with other hardware components or software drivers. This can result in system instability, crashes, or functionality limitations if the new part is not properly supported by the laptop's architecture.
- Increased Power Consumption: High-performance laptop parts, such as powerful CPUs and dedicated GPUs, consume more power, leading to reduced battery life and increased energy costs. Users may need to compromise between performance and battery life depending on their usage patterns and preferences.
- Cost: Upgrading laptop parts to the latest technology can be costly, especially for high-end components such as top-tier CPUs, GPUs, or high-capacity SSDs. Users must weigh the benefits of improved performance against the cost of upgrading and consider whether the investment is justified based on their needs and usage.
- Environmental Impact: The production and disposal of laptop parts can have a negative impact on the environment. Manufacturing processes, resource extraction, and electronic waste generated from obsolete or discarded laptop parts contribute to pollution, resource depletion, and landfill accumulation if not properly managed or recycled.
While advancements in laptop parts offer numerous benefits such as improved performance, productivity, and portability, they also present challenges such as overheating, compatibility issues, increased power consumption, cost, and environmental concerns. Users should carefully consider these factors when upgrading or using their laptops to optimize their experience while minimizing potential drawbacks.
What are the examples of Laptop Parts, list and explain them in details
Here are some examples of laptop parts along with explanations of their functions:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU):
- Function: The CPU, often referred to as the brain of the computer, performs calculations, executes instructions, and manages data flow within the system.
- Explanation: The CPU interprets instructions from software programs, processes data, and coordinates tasks performed by other components. It plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance and responsiveness of the laptop.
- Random Access Memory (RAM):
- Function: RAM serves as temporary storage for data and program instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly during operation.
- Explanation: When a program is running, its data and instructions are loaded into RAM for quick access by the CPU. Higher RAM capacities allow for smoother multitasking and faster data processing, enhancing overall system performance.
- Storage Devices (e.g., SSD, HDD):
- Function: Storage devices store data, applications, and the operating system for long-term use.
- Explanation: Solid-state drives (SSDs) and hard disk drives (HDDs) are the two primary types of storage devices found in laptops. SSDs offer faster data access speeds and are more resistant to physical shock, while HDDs provide larger storage capacities at a lower cost per gigabyte.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU):
- Function: The GPU is responsible for rendering images, videos, and graphical elements on the laptop's display.
- Explanation: GPUs offload graphical processing tasks from the CPU, allowing for smoother graphics rendering and improved performance in tasks such as gaming, video editing, and graphic design. Dedicated GPUs offer higher performance compared to integrated graphics solutions.
- Display Panel:
- Function: The display panel provides the visual interface for interacting with the laptop, presenting text, images, videos, and graphical user interfaces.
- Explanation: Display panels come in various types, including LCD, LED, OLED, and touchscreen displays. Factors such as resolution, color accuracy, refresh rate, and size influence the viewing experience and overall usability of the laptop.
- Input Devices (e.g., Keyboard, Touchpad):
- Function: Input devices allow users to interact with the laptop and input commands or data.
- Explanation: Keyboards enable users to input text and commands, while touchpads and pointing devices control cursor movement on the screen. Touchscreen displays offer additional input options through touch gestures and stylus input, enhancing user flexibility and productivity.
- Battery:
- Function: The battery provides electrical power to the laptop, allowing it to operate independently of external power sources.
- Explanation: Lithium-ion batteries power laptops, enabling them to run for hours on a single charge. Battery capacity, measured in watt-hours (Wh), determines the duration of battery life, while fast-charging technology reduces recharge times for increased convenience.
- Chassis and Cooling System:
- Function: The chassis provides structural support and protection for internal components, while the cooling system regulates temperatures to prevent overheating.
- Explanation: The laptop chassis houses and protects internal components from physical damage, while cooling systems consisting of heat pipes, heat sinks, and fans dissipate heat generated during operation, maintaining optimal performance and prolonging component lifespan.
These examples illustrate the diverse range of components that make up a laptop and highlight their respective functions in facilitating computing tasks and providing a seamless user experience.
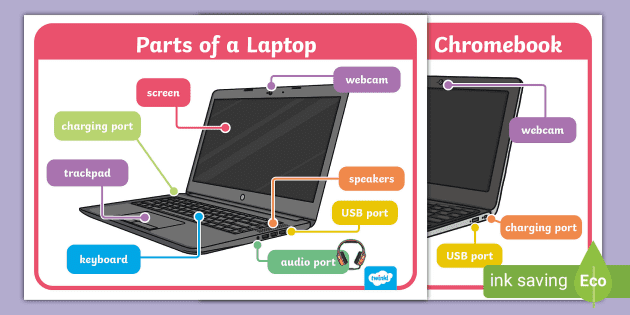
What are the parts in laptop?
Laptops consist of various components, each playing a crucial role in the device's functionality. Here's a comprehensive list of the main parts typically found in laptops:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is the primary processing unit of the laptop, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): RAM provides temporary storage for data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly during operation.
- Storage Device: Laptops typically include storage devices such as solid-state drives (SSDs) or hard disk drives (HDDs) to store data, applications, and the operating system.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): The GPU handles graphical tasks, rendering images, videos, and 3D graphics on the laptop's display.
- Display Panel: The display panel presents visual output to the user, allowing them to view text, images, videos, and graphical user interfaces.
- Input Devices:
- Keyboard: The keyboard enables users to input text and commands into the laptop.
- Touchpad: The touchpad provides a pointing device for controlling cursor movement on the screen.
- Touchscreen: Some laptops feature touchscreen displays, allowing users to interact directly with the screen using touch gestures.
- Pointing Stick: Some laptops include a pointing stick (e.g., TrackPoint), offering an alternative method for cursor navigation.
- Battery: The battery provides power to the laptop, allowing it to operate independently of external power sources.
- Chassis and Housing: The chassis houses and protects internal components, providing structural support and durability to the laptop.
- Cooling System: Laptops incorporate cooling systems consisting of heat pipes, heat sinks, and fans to dissipate heat generated by internal components and prevent overheating.
- Ports and Connectivity: Laptops feature various ports and connectivity options for connecting peripherals, external displays, and networking devices. Common ports include USB, HDMI, Ethernet, and headphone jacks.
- Wireless Communication: Laptops include wireless communication capabilities such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth for wireless internet connectivity and peripheral device connectivity.
- Motherboard: The motherboard serves as the main circuit board that connects and integrates all internal components of the laptop.
- Speakers and Audio System: Laptops include built-in speakers and audio systems for playing sound and multimedia content.
- Webcam: Many laptops feature built-in webcams for video conferencing, video calls, and capturing photos and videos.
- Microphone: Laptops may include built-in microphones for voice input, audio recording, and video calls.
These are the primary parts typically found in laptops, although specific configurations and features may vary depending on the manufacturer, model, and intended use of the device.
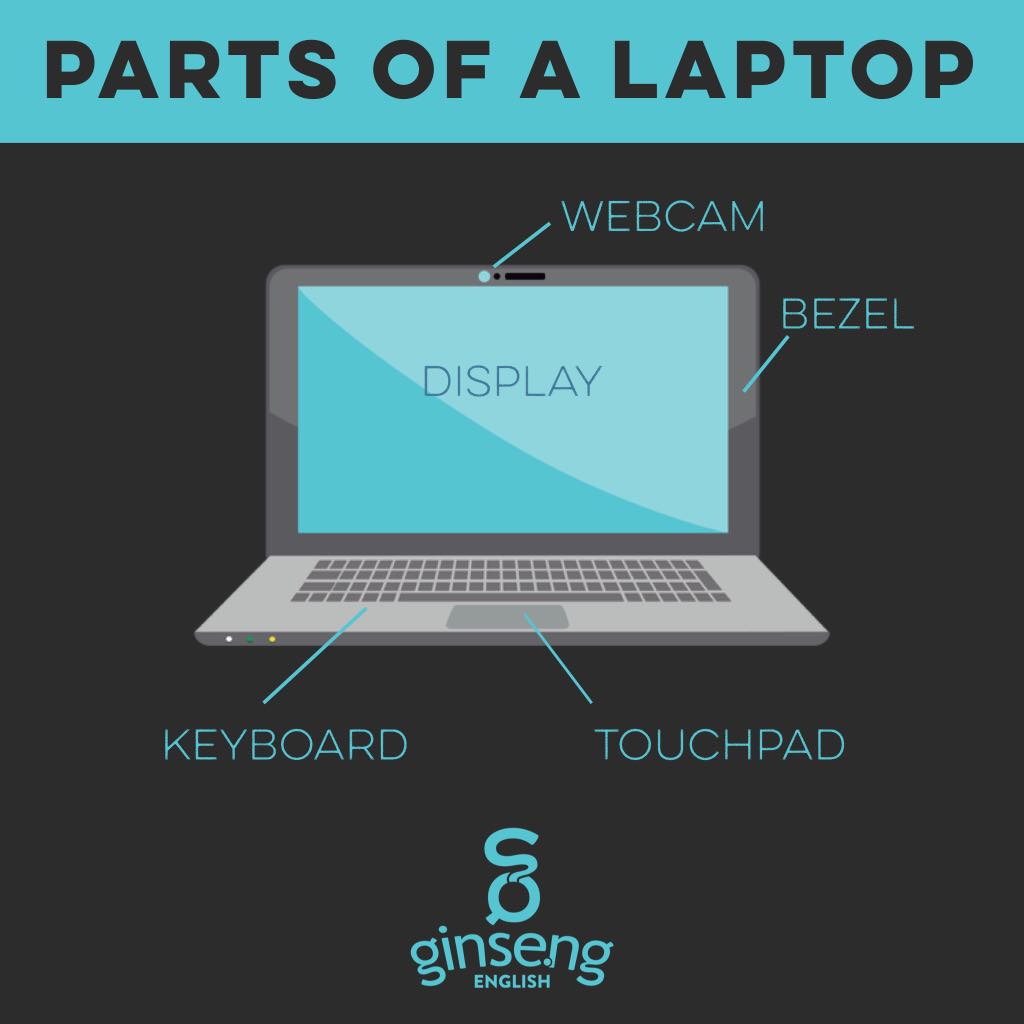
What is inside a laptop?
Inside a laptop, you'll find a variety of components working together to provide functionality and performance. Here's a breakdown of what you'll typically find inside a laptop:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is the "brain" of the laptop, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. It handles tasks such as running programs, processing data, and managing system resources.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): RAM provides temporary storage for data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly during operation. It allows for multitasking and smooth performance by providing fast access to frequently used data.
- Storage Device: Laptops contain storage devices such as solid-state drives (SSDs) or hard disk drives (HDDs) to store data, applications, and the operating system. These devices vary in capacity and speed, with SSDs generally offering faster performance than HDDs.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): The GPU is responsible for rendering images, videos, and 3D graphics on the laptop's display. It handles graphical tasks, such as gaming, video playback, and graphic design applications.
- Display Panel: The display panel presents visual output to the user, allowing them to view text, images, videos, and graphical user interfaces. Display panels come in various types, including LCD, LED, OLED, and touchscreen displays.
- Input Devices:
- Keyboard: The keyboard enables users to input text and commands into the laptop. Keyboards vary in layout and design, with some laptops featuring backlit keyboards for use in low-light environments.
- Touchpad: The touchpad provides a pointing device for controlling cursor movement on the screen. It supports gestures such as scrolling, zooming, and tapping for enhanced navigation.
- Touchscreen: Some laptops feature touchscreen displays, allowing users to interact directly with the screen using touch gestures. Touchscreens are commonly found in 2-in-1 convertible laptops and tablets.
- Battery: The battery provides power to the laptop, allowing it to operate independently of external power sources. Laptop batteries vary in capacity and lifespan, with newer models offering longer battery life and faster charging times.
- Chassis and Housing: The chassis houses and protects internal components, providing structural support and durability to the laptop. It also includes ports and connectors for external devices and peripherals.
- Cooling System: Laptops incorporate cooling systems consisting of heat pipes, heat sinks, and fans to dissipate heat generated by internal components. Cooling systems prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance during intensive tasks.
- Ports and Connectivity: Laptops feature various ports and connectivity options for connecting peripherals, external displays, and networking devices. Common ports include USB, HDMI, Ethernet, and headphone jacks.
- Wireless Communication: Laptops include wireless communication capabilities such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth for wireless internet connectivity and peripheral device connectivity.
- Motherboard: The motherboard serves as the main circuit board that connects and integrates all internal components of the laptop. It provides power distribution, data communication, and control functions for the entire system.
These components work together to provide functionality and performance, allowing users to perform tasks such as browsing the internet, running software applications, playing games, and creating content on their laptops.
What are the three main features of a laptop?
The three main features of a laptop are:
- Portability: One of the most significant features of a laptop is its portability. Laptops are designed to be compact and lightweight, allowing users to carry them easily from one location to another. Unlike desktop computers, laptops do not require a fixed workspace and can be used anywhere, whether at home, in the office, or while traveling. The portability of laptops enables users to stay productive and connected while on the go, making them ideal for students, professionals, and anyone who needs to work or access information outside of a traditional office environment.
- Battery Power: Another key feature of laptops is their ability to operate on battery power. Laptops are equipped with rechargeable batteries that allow them to function without being plugged into a power outlet for a certain period. The battery life of a laptop varies depending on factors such as usage intensity, display brightness, and system configuration. However, modern laptops typically offer several hours of battery life on a single charge, providing users with flexibility and convenience to use their devices untethered from power sources. Battery power is essential for users who need to work or access information while on the move or in locations where power outlets are not readily available.
- All-in-One Design: Laptops are designed to integrate all the essential components of a computer into a single, compact device. Unlike desktop computers, which consist of separate components such as the monitor, keyboard, and CPU tower, laptops combine the display, keyboard, touchpad or pointing device, and internal components (CPU, RAM, storage, etc.) into a single unit. This all-in-one design makes laptops convenient and easy to set up and use, requiring minimal space and eliminating the need for multiple cables and peripherals. Additionally, the compact form factor of laptops allows for greater flexibility in terms of placement and usage, making them suitable for various environments and purposes.
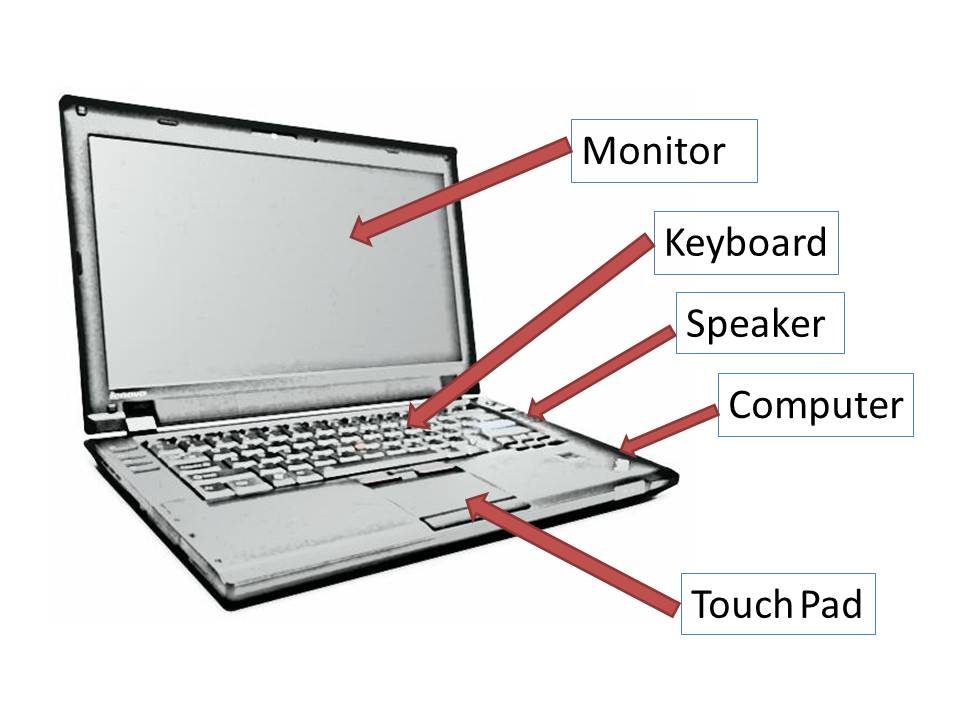
What are the functions of a laptop computer?
Laptop computers serve a multitude of functions, catering to various needs and requirements of users. Here are some of the primary functions of a laptop computer:
- General Computing: Laptops provide users with the ability to perform general computing tasks such as web browsing, email communication, document editing, and file management. They serve as versatile tools for accessing information, creating content, and managing personal or professional tasks.
- Work and Productivity: Laptops are widely used for work and productivity purposes, enabling users to perform tasks such as word processing, spreadsheet management, presentations, and data analysis. They serve as portable workstations for professionals in various industries, including business, education, healthcare, and creative fields.
- Entertainment: Laptops offer a wide range of entertainment options, including streaming movies and TV shows, listening to music, playing video games, and browsing social media. They provide users with access to multimedia content and online entertainment platforms, allowing for leisure activities and relaxation.
- Education and Learning: Laptops play a significant role in education and learning, providing students with access to educational resources, online courses, digital textbooks, and collaborative tools. They serve as essential tools for research, studying, and academic projects, enabling students to learn and engage in educational activities both inside and outside the classroom.
- Communication: Laptops facilitate communication and collaboration through various channels, including email, instant messaging, video conferencing, and social networking. They serve as communication hubs for staying in touch with family, friends, colleagues, and clients, whether through written messages, voice calls, or video chats.
- Creativity and Multimedia Production: Laptops are used for creative endeavors such as graphic design, photo editing, video editing, music production, and content creation. They provide users with powerful software tools and hardware capabilities for expressing their creativity, editing multimedia content, and producing professional-quality media.
- Research and Information Gathering: Laptops enable users to conduct research, gather information, and access online resources on a wide range of topics. They serve as portable libraries, granting users instant access to vast amounts of information, scholarly articles, research papers, and academic databases.
- Remote Work and Telecommuting: Laptops facilitate remote work and telecommuting by allowing users to perform their job duties from any location with internet access. They enable professionals to work remotely, collaborate with colleagues, attend virtual meetings, and access corporate resources securely from home, co-working spaces, or while traveling.
- Personal Organization and Management: Laptops serve as personal organizers and management tools, helping users stay organized, manage schedules, track tasks, and maintain personal and professional productivity. They offer features such as calendars, to-do lists, reminders, and note-taking applications for managing daily activities and priorities.
- Accessibility and Assistive Technology: Laptops can be customized and equipped with accessibility features and assistive technologies to accommodate users with disabilities or special needs. These features include screen readers, magnification tools, speech recognition software, and alternative input devices, enabling users to access and interact with the computer effectively.
Overall, laptops offer a wide range of functions and capabilities, making them indispensable tools for work, learning, communication, creativity, entertainment, and personal organization in today's digital world.
What are the 5 major functions of a computer?
Computers serve various functions that are crucial in both personal and professional contexts. Here are the five major functions of a computer:
- Data Processing: One of the primary functions of a computer is to process data. This involves performing calculations, executing instructions, and manipulating data to produce meaningful output. Computers can process vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, making them essential for tasks such as mathematical calculations, data analysis, and scientific simulations.
- Storage: Computers store data and information in various forms, including text, images, videos, and software programs. They use storage devices such as hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) to store data permanently or temporarily. Storage allows users to save files, access information, and retrieve data for future use.
- Communication: Computers enable communication between users and systems through various channels, including the internet, local networks, and peripheral devices. They facilitate email communication, instant messaging, video conferencing, and social networking, allowing users to connect and interact with others worldwide. Computers also enable communication between different hardware components and software programs within the system.
- Automation: Computers automate repetitive tasks and processes, reducing manual effort and increasing efficiency. They can perform automated tasks such as data entry, file management, system backups, and software updates. Automation streamlines workflows, improves productivity, and frees up time for users to focus on more complex or creative tasks.
- Information Retrieval: Computers retrieve information and provide access to vast amounts of data stored locally or on the internet. They allow users to search for information, browse websites, access online databases, and retrieve documents and multimedia content. Information retrieval is essential for research, learning, decision-making, and staying informed about current events and trends.
These five major functions of a computer—data processing, storage, communication, automation, and information retrieval—form the foundation of modern computing and enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks and applications in various domains and industries.
What are 10 uses of a laptop?
Laptops are versatile devices that can be used for a wide range of purposes. Here are ten common uses of a laptop:
- Work and Productivity: Laptops are commonly used for work-related tasks such as word processing, spreadsheet management, presentations, email communication, and project management. They serve as portable workstations for professionals in various industries, enabling productivity from any location.
- Web Browsing: Laptops provide access to the internet, allowing users to browse websites, search for information, read news articles, shop online, and interact with online communities and social media platforms.
- Entertainment: Laptops offer a variety of entertainment options, including streaming movies and TV shows, listening to music, playing video games, and viewing photos and videos. They provide users with on-the-go entertainment experiences, whether at home, during travel, or in leisure time.
- Education and Learning: Laptops play a significant role in education and learning, providing students with access to educational resources, online courses, digital textbooks, and collaborative tools. They facilitate research, studying, and academic projects, enabling distance learning and self-paced learning experiences.
- Communication: Laptops facilitate communication and collaboration through various channels, including email, instant messaging, video conferencing, and social networking. They serve as communication hubs for staying in touch with family, friends, colleagues, and clients, whether for personal or professional purposes.
- Creative Endeavors: Laptops are used for creative endeavors such as graphic design, photo editing, video editing, music production, and content creation. They provide users with powerful software tools and hardware capabilities for expressing their creativity, editing multimedia content, and producing professional-quality media.
- Research and Information Gathering: Laptops enable users to conduct research, gather information, and access online resources on a wide range of topics. They serve as portable libraries, granting users instant access to vast amounts of information, scholarly articles, research papers, and academic databases.
- Personal Organization and Management: Laptops serve as personal organizers and management tools, helping users stay organized, manage schedules, track tasks, and maintain personal and professional productivity. They offer features such as calendars, to-do lists, reminders, and note-taking applications for managing daily activities and priorities.
- Remote Work and Telecommuting: Laptops facilitate remote work and telecommuting by allowing users to perform their job duties from any location with internet access. They enable professionals to work remotely, collaborate with colleagues, attend virtual meetings, and access corporate resources securely from home, co-working spaces, or while traveling.
- Gaming: Laptops are used for gaming, offering users the ability to play a wide variety of video games ranging from casual and indie titles to graphically-intensive AAA games. Gaming laptops are equipped with dedicated graphics cards and high-performance hardware to deliver smooth gaming experiences on the go.
These are just a few examples of the many uses of laptops, highlighting their versatility and importance in today's digital age.



