Empowering Communication: The Evolving Landscape of Speech Aid Technology
A speech aid is a device designed to assist individuals with communication challenges, enabling them to express themselves effectively. These aids come in various forms, ranging from simple communication boards to sophisticated electronic devices. Advantages include improved communication, enhanced independence, and increased social interaction. However, challenges such as cost, a learning curve, and potential social stigma may be associated with their use. Overall, speech aids play a crucial role in fostering inclusivity and empowering individuals facing speech difficulties.
Advantages and Challenges of Speech Aids.

Communication is a fundamental aspect of human interaction, but for those facing speech challenges, technology has become a powerful ally in breaking down barriers. This article explores the cutting-edge advancements in speech aid technology, shedding light on how these innovations are transforming lives and fostering inclusivity.
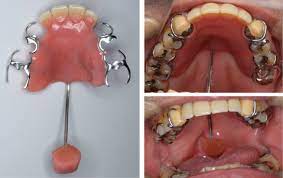
The Rise of Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC):
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) has witnessed a remarkable surge in adoption. According to recent studies by the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA), over 2.8 million individuals in the United States alone rely on AAC devices to enhance their communication capabilities. The evolution of AAC technology has paved the way for customizable communication boards, dynamic display devices, and intuitive applications.
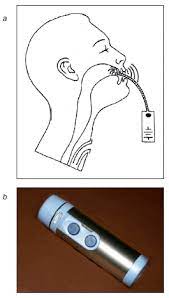
Revolutionizing Communication with AI-Powered Speech:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a game-changer in the realm of speech aid. Modern Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems, driven by advanced AI algorithms, offer more natural and expressive voices. Companies like Google and Microsoft have made significant strides in developing AI-driven speech synthesis, providing users with a more personalized and human-like communication experience.
Breaking Physical Barriers: Eye Gaze Technology:
For individuals with severe motor impairments, eye gaze technology has emerged as a transformative solution. The ability to control a communication device through eye movements has opened up new possibilities. Recent data from the Assistive Technology Industry Association (ATIA) reveals that eye gaze technology has seen a 30% increase in adoption over the past two years.
Mobile Apps: A Pocket-Sized Revolution:
Mobile applications designed for speech aid have become widely accessible tools. Apps like Proloquo2Go and Touch Chat empower users by turning smartphones and tablets into portable communication devices. The convenience and versatility of these apps have contributed to their popularity, with downloads surpassing the 10 million mark globally.
Inclusive Education: Integrating Speech Aid in Schools:
The impact of speech aid technology is particularly evident in the educational landscape. Schools worldwide are increasingly integrating AAC devices into classrooms, ensuring that students with communication difficulties can actively participate in lessons. Research from the National Center for Special Education Research (NCSER) indicates a positive correlation between the use of speech aid technology in schools and academic achievement among students with communication disorders.
Challenges and Future Directions:
While speech aid technology has made remarkable strides, challenges persist. Affordability, accessibility, and ongoing support are areas that demand attention. However, ongoing research and collaboration within the assistive technology community are actively addressing these challenges.
The types of speech Aid:

There are various types of speech aids designed to assist individuals with communication difficulties. Here is a list of common types:
- Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) Devices:
- Communication Boards: Physical boards with symbols or pictures that users can point to for communication.
- Electronic Devices: Tablets or dedicated devices with AAC apps, allowing users to select symbols or type out messages that are then spoken by the device.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) Software:
- Software applications that convert written text into spoken words. Users can input text, and the software vocalizes it.
- Speech Generating Devices (SGDs):
- Dedicated devices designed specifically for generating speech. These devices often have customizable vocabularies and can be controlled through various input methods like touchscreens, switches, or eye gaze.
- Voice Recognition Software:
- Enables users to control a computer or device through spoken commands. This can be particularly useful for individuals with mobility challenges.
- Mobile Apps:
- Various apps available on smartphones or tablets that provide speech assistance, ranging from basic communication tools to advanced AAC solutions.
- Eye Gaze Technology:
- Systems that allow users to control a computer or communication device by tracking their eye movements. This is especially helpful for individuals with limited mobility.
- Speech Therapy Software:
- Programs designed to assist with speech therapy and language development. These can be used independently or with the guidance of a speech-language pathologist.
- Customized Communication Devices:
- Some individuals may require specialized devices tailored to their specific needs, considering factors like the user's motor skills, cognitive abilities, and communication goals.
- Symbol-Based Systems:
- Systems that use symbols or pictures to represent words or concepts, aiding individuals who may struggle with text-based communication.
- Gesture-Based Communication:
- Involves using gestures or sign language to communicate, particularly for individuals who may have difficulty with verbal communication.
- Brain-Computer Interface (BCI):
- Emerging technology that allows individuals to control devices or communicate using brain signals. While still in development, BCIs hold promise for individuals with severe physical limitations.
It's important to note that the choice of a speech aid depends on the individual's specific needs, abilities, and preferences. Additionally, advancements in technology continue to contribute to the expansion and improvement of speech aid options.
Benefits of speech Aid:
Speech aids offer numerous benefits to individuals facing communication challenges, whether due to developmental disorders, neurological conditions, injuries, or other factors. Here are some key benefits of using speech aids:
- Enhanced Communication:
- The primary and most significant benefit of speech aids is improved communication. These devices empower individuals to express themselves, share thoughts, and engage in conversations, fostering a sense of connection with others.
- Increased Independence:
- Speech aids enable greater independence by providing individuals with the means to communicate their needs, make choices, and participate actively in various aspects of life, including education, work, and social interactions.
- Boosted Confidence:
- The ability to communicate effectively can significantly boost self-confidence. Speech aids give individuals the tools to express themselves, contributing to increased self-esteem and a sense of accomplishment.
- Facilitated Social Interactions:
- With speech aids, individuals can more easily participate in social interactions. This can lead to the formation of friendships, improved relationships, and a greater sense of belonging within the community.
- Support for Education:
- Speech aids play a crucial role in educational settings. They help students with communication difficulties fully engage in the learning process, participate in classroom activities, and interact with peers and teachers.
- Assistance in Daily Activities:
- Speech aids assist individuals in conveying their needs and preferences in daily activities, such as making choices about food, expressing discomfort or pain, and seeking assistance when required.
- Empowerment for Individuals with Speech Disorders:
- Individuals with speech disorders, such as apraxia or stuttering, can benefit from speech aids to enhance their communication abilities. These aids provide tools for practicing and refining speech skills.
- Flexibility and Adaptability:
- Many speech aids offer customization and adaptability, allowing users to tailor the device to their specific needs. This ensures a personalized and effective communication experience.
- Inclusion in Work Environments:
- Speech aids contribute to the inclusion of individuals with communication challenges in the workforce. They provide a means for effective communication, allowing these individuals to pursue various career paths and contribute to their workplace.
- Family and Caregiver Support:
- Speech aids assist family members and caregivers in understanding the needs and desires of individuals with communication difficulties. This leads to improved caregiving and a more supportive family environment.
- Early Intervention and Development:
- For children with speech and language delays, speech aids can play a crucial role in early intervention, supporting language development and communication skills during critical developmental stages.
- Integration of Technology:
- The use of speech aids incorporates technology into communication, helping individuals stay connected in a world where digital communication is increasingly prevalent.
Overall, speech aids contribute significantly to improving the quality of life for individuals with communication challenges, promoting inclusivity, and empowering them to participate more fully in society.
Here is a list of purposes served by speech aids:

- Facilitating Communication:
- The primary purpose of speech aids is to assist individuals in expressing themselves and communicating effectively, especially when traditional verbal communication is challenging.
- Enhancing Independence:
- Speech aids empower individuals to communicate their needs and preferences independently, reducing reliance on others for everyday tasks.
- Supporting Social Interaction:
- Speech aids enable individuals to engage in social interactions, fostering connections with family, friends, and the community.
- Promoting Inclusion in Education:
- Speech aids help students with communication difficulties actively participate in educational settings, enhancing their learning experience and social integration.
- Assisting in Daily Living Activities:
- Speech aids aid individuals in conveying their desires, making choices, and participating in daily activities such as mealtime, personal care, and recreational pursuits.
- Enabling Work Participation:
- In professional environments, speech aids facilitate effective communication, enabling individuals with speech challenges to engage in various job roles and activities.
- Addressing Speech and Language Development:
- For individuals, especially children, speech aids can support speech and language development, providing tools for practicing and improving communication skills.
- Providing Alternative Communication Methods:
- Speech aids offer alternative methods of communication for those who may have difficulty with traditional speech, such as individuals with apraxia, dysarthria, or non-verbal individuals.
- Boosting Confidence and Self-Esteem:
- The ability to communicate successfully using speech aids can enhance an individual's confidence and self-esteem, contributing to a positive self-perception.
- Customization for Individual Needs:
- Speech aids often allow for customization to meet the specific needs, preferences, and abilities of each individual, ensuring a more personalized communication experience.
- Facilitating Interaction with Technology:
- Speech aids integrate with technology, allowing users to interact with computers, tablets, and other devices through speech or alternative input methods.
- Supporting Caregivers and Family Communication:
- Speech aids assist caregivers and family members in understanding and responding to the communication needs of their loved ones, strengthening family bonds.
- Adapting to Changing Needs:
- Many speech aids are flexible and adaptable, accommodating changes in the user's abilities, preferences, and communication requirements over time.
- Promoting Inclusive Access to Information:
- Speech aids contribute to inclusive access to information and communication technologies, ensuring that individuals with speech challenges can participate fully in the digital age.
These purposes collectively highlight the broad impact of speech aids in improving the quality of life for individuals with communication difficulties, fostering inclusion, and promoting active participation in various aspects of life.
Features of speech Aid:
The features of speech aids can vary depending on the type and complexity of the device. Here are common features found in various speech aids.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS):
- Converts typed or inputted text into spoken words, allowing users to communicate through written messages.
- Symbol-Based Communication:
- Utilizes symbols or pictures representing words or phrases, suitable for individuals with limited literacy skills or non-verbal communication needs.
- Customizable Vocabulary:
- Allows users or caregivers to personalize the vocabulary and content to match individual preferences and communication requirements.
- Voice Options:
- Offers a variety of voices and accents, enabling users to choose a voice that suits their preferences and makes communication more comfortable.
- Dynamic Display:
- Incorporates touchscreens or dynamic displays that change based on the context, providing a more versatile and adaptable communication experience.
- Switch Access:
- Supports input through external switches, which can be beneficial for individuals with limited motor skills or mobility challenges.
- Eye Gaze Technology:
- Integrates eye tracking to control the device, allowing users to make selections or generate speech by using their eye movements.
- Word Prediction:
- Predicts words or phrases as the user types, speeding up communication and reducing the effort required for input.
- Environmental Control:
- Integrates with home automation systems, allowing users to control their environment (lights, doors, etc.) through the speech aid.
- Multi-Modal Input:
- Supports various input methods, such as touch, switch, eye gaze, and voice commands, providing flexibility for users with diverse needs.
- Phonetic and Semantic Prediction:
- Predicts words or phrases based on the sounds or meanings of the entered text, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in communication.
- Integration with Mobile Devices:
- Connects with smartphones or tablets, allowing users to use familiar devices and access communication tools on the go.
- Communication Boards:
- Physical or digital boards with grids of symbols or pictures that users can point to or touch to communicate.
- Educational Games and Activities:
- Includes interactive games and activities to support speech and language development, particularly beneficial for children.
- Data Logging and Reporting:
- Records usage data and generates reports, offering insights for caregivers, therapists, and users to monitor progress and identify communication patterns.
- User Profiles:
- Supports multiple user profiles, allowing the speech aid to be customized for different individuals who may share the device.
- Integration with Augmented Reality (AR):
- Utilizes AR features to enhance the user experience and provide interactive and immersive communication opportunities.
- Remote Programming and Updates:
- Allows for remote programming and updates, ensuring that the device can be customized and maintained without requiring physical access.
These features collectively contribute to creating a comprehensive and effective communication solution for individuals with speech and language challenges. The choice of features depends on the specific needs and preferences of the user.
Cost and value of speech Aid:
The cost and value of speech aids can vary widely depending on factors such as the type of aid, its features, and the brand. Here are some considerations regarding the cost and value of speech aids:
Factors Influencing Cost:
- Type of Speech Aid:
- The type of speech aid significantly affects its cost. Dedicated devices with advanced features, such as eye gaze technology and environmental control, tend to be more expensive than basic communication boards or simple text-to-speech apps.
- Features and Technology:
- Advanced features, such as eye gaze tracking, dynamic displays, and integration with other technologies, can contribute to a higher cost. Cutting-edge technology and customization options may also influence the price.
- Brand and Manufacturer:
- Different brands and manufacturers offer a range of speech aids at varying price points. Established brands with a reputation for reliability and innovation may command higher prices.
- Customization and Adaptability:
- Devices that offer a high degree of customization, adaptability, and versatility may be more expensive. This includes features like customizable vocabularies, multiple input methods, and personalized settings.
- Accessibility and Compatibility:
- Speech aids that are compatible with a wide range of devices and operating systems may be priced higher. Accessibility features, such as switch compatibility and cross-platform integration, can influence the cost.
- Technical Support and Warranty:
- The availability of robust technical support, training, and warranty services can contribute to the overall cost. Devices with extensive support services may be priced higher for the added value they provide.
Factors Influencing Value:
- Effectiveness in Communication:
- The primary value of a speech aid lies in its effectiveness in facilitating communication. A high-quality speech aid that meets the user's communication needs adds significant value to their daily life.
- User-Friendly Design:
- Speech aids that are easy to use and have an intuitive design provide added value, especially for individuals with varying levels of technical proficiency.
- Customization for Individual Needs:
- Devices that can be tailored to the specific needs, preferences, and abilities of the user add substantial value. Customization ensures a more personalized and effective communication experience.
- Durability and Reliability:
- The durability and reliability of a speech aid contribute to its overall value. A robust device that withstands regular use and offers long-term functionality provides better value for the investment.
- Integration with Daily Activities:
- Speech aids that seamlessly integrate with daily activities, including education, work, and leisure, enhance their overall value. This includes features like environmental control and mobile device integration.
- Support Services:
- Adequate technical support, training, and warranty services add significant value. These services ensure that users can effectively use and maintain their speech aids, addressing any issues that may arise.
- Educational and Therapeutic Support:
- Speech aids that include educational games, activities, or therapeutic support contribute to the user's overall development, especially in the case of children with speech and language challenges.
- User Satisfaction and Outcomes:
- Ultimately, the value of a speech aid is reflected in user satisfaction and the outcomes achieved. If the device effectively meets communication goals and improves the user's quality of life, it provides substantial value.
It's important for individuals and caregivers to carefully assess both the cost and the value of a speech aid, considering the specific needs and goals of the user. The goal is to find a balance that ensures the aid is not only affordable but also highly effective in meeting the user's communication requirements.
Caution:

When considering and using speech aids, it's important to be aware of certain cautionary points to ensure their effective and safe use. Here are some cautionary considerations:
- Consultation with Professionals:
- Before selecting or using a speech aid, it's crucial to consult with speech-language pathologists, healthcare professionals, or assistive technology specialists. They can provide guidance on the most suitable options based on the individual's specific needs and abilities.
- Individual Assessment:
- Each person has unique communication challenges, and what works well for one individual may not be suitable for another. An individualized assessment is essential to determine the most appropriate speech aid.
- Training and Familiarization:
- Adequate training is essential for both users and caregivers to ensure the proper use of the speech aid. Understanding its features, customization options, and maintenance procedures is crucial for effective communication.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Speech aids, particularly electronic devices, may require regular maintenance to ensure optimal functionality. This includes software updates, battery replacement, and addressing any technical issues promptly.
- Consideration of Changing Needs:
- Individuals' communication needs may change over time due to factors such as evolving abilities or health conditions. Regular reassessment and potential adjustments to the speech aid are important to meet changing requirements.
- Integration with Other Therapies:
- Speech aids are often part of a broader communication and therapy plan. It's important to integrate the use of speech aids with other therapeutic interventions, such as speech therapy, to maximize effectiveness.
- Monitoring User Comfort:
- Pay attention to the user's comfort and preferences. Some individuals may find certain features or input methods more suitable than others. Regular feedback and adjustments can enhance the overall user experience.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity:
- Ensure that the chosen speech aid is accessible and inclusive. Consider factors such as compatibility with other devices, adaptability to different environments, and the provision of alternative input methods.
- Privacy and Security:
- For speech aids that involve digital communication, consider privacy and security aspects. Ensure that the device has appropriate measures in place to protect sensitive information and maintain user privacy.
- Age-Appropriate Solutions:
- For children, it's important to choose age-appropriate speech aids that align with their developmental stage and communication needs. Regular reassessment is crucial as the child grows and their abilities evolve.
- Affordability and Funding:
- Speech aids can vary widely in cost, and it's important to consider affordability. Explore potential funding sources, including insurance, grants, or assistance programs that may help cover the costs.
- Backup Communication Methods:
- While speech aids are valuable, it's prudent to have backup communication methods in place. This could include low-tech alternatives or strategies in case the primary device is unavailable or malfunctions.
By approaching the use of speech aids with careful consideration and regular assessment, individuals and caregivers can navigate potential challenges and optimize the benefits of these communication tools. Ongoing collaboration with professionals and a proactive approach to user needs contribute to a positive and effective experience with speech aids.
Addressing Common Questions:
- What does speech aid mean?
- A speech aid refers to any device or tool designed to assist individuals with communication difficulties, helping them express themselves verbally or through alternative means.
- What are the devices used to aid speech?
- Devices used to aid speech include Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) devices, text-to-speech software, communication boards, speech-generating devices, and other tools designed to enhance communication for individuals with speech challenges.
- What is communication aid?
- A communication aid is a broader term that encompasses various tools and strategies, including speech aids, used to support and enhance communication for individuals with speech or language difficulties.
- What are examples of speech-generating devices?
- Examples of speech-generating devices include dedicated communication devices (such as those by Tobii Dynavox), tablets with AAC apps (like Proloquo2Go), and electronic communication boards that generate speech output.
- What is a speech visual aid?
- A speech visual aid typically refers to visual supports, charts, or images used to complement or enhance spoken communication. It can include visual cues, symbols, or pictures that aid understanding or reinforce verbal messages.
- What is aid called?
- The term "aid" can refer to various types of support or assistance. In the context of communication, it might specifically refer to communication aids or devices that assist individuals with speech challenges.
- What is a speech device called?
- A speech device is often referred to as a speech aid or a speech-generating device. These devices can be electronic or non-electronic tools designed to help individuals communicate effectively.
- How are speech-generating devices used?
- Speech-generating devices are used by individuals who may have difficulty with verbal communication. Users can input text, symbols, or use alternative methods (such as eye gaze or switches), and the device generates spoken output to convey their messages.
- What are three communication devices examples?
- Three examples of communication devices are:
- Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) devices
- Text-to-speech software
- Communication boards or visual aids
- Three examples of communication devices are:
- What are the 5 modern communication devices?
- Five modern communication devices include:
- Smartphones
- Tablets
- Laptops and computers
- Smartwatches
- Voice-activated smart speakers
- Five modern communication devices include:
- What are the three main types of communication?
- The three main types of communication are verbal communication (spoken words), nonverbal communication (body language, gestures), and written communication.
- Is TV a communication device?
- While TV can be a form of communication media, it is not typically considered a communication device in the same sense as devices designed to aid or facilitate direct interpersonal communication.
- What is the main goal of presentation aid?
- The main goal of a presentation aid is to enhance the audience's understanding and retention of information. Visual aids, multimedia, and other presentation tools are used to support and complement spoken communication during presentations.
- How do you use aid?
- The use of aid depends on the context. For communication aids, individuals may use them by selecting symbols, typing text, or using alternative input methods to convey messages. Proper training and familiarity with the aid are essential.
- What is the exact meaning of speech?
- Speech refers to the expression of thoughts, ideas, or emotions through spoken words. It is a form of verbal communication that involves the production of sounds using the vocal apparatus.
- What are the functions of communication aid?
- The functions of communication aids include facilitating expression, enhancing comprehension, promoting independence, fostering social interaction, and providing alternative means of communication for individuals with speech challenges.
- What is the device that helps people speak?
- A device that helps people speak is commonly referred to as a speech aid or a speech-generating device. These devices assist individuals who may have difficulty with natural speech in expressing themselves.
- What is an example of a speech-generating device?
- An example of a speech-generating device is the Tobii Dynavox communication device, which includes features like eye gaze technology and customizable communication boards to assist individuals with speech challenges.
- What is a quick talker device?
- A QuickTalker is a brand of speech-generating devices designed for easy and quick communication. These devices typically feature pre-programmed messages or phrases for efficient communication.
- What is a SpeechVive device?
- SpeechVive is a wearable device designed to help individuals with Parkinson's disease improve their speech volume and clarity. It uses a reflexive response to ambient noise to trigger louder and clearer speech.
The price of items can vary based on factors like location, seller, and availability. For accurate and up-to-date pricing information, I recommend checking with local retailers, online marketplaces, or contacting distributors and manufacturers directly.
Advantages and disadvantages of speech aid:
Advantages.
- Improved Communication:
- The primary advantage of speech aids is that they enhance communication for individuals with speech challenges, allowing them to express themselves more effectively.
- Enhanced Independence:
- Speech aids empower users, promoting independence in communication and reducing reliance on others for conveying messages.
- Increased Social Interaction:
- By facilitating communication, speech aids contribute to improved social interactions, allowing users to engage more fully in conversations and activities.
- Support for Education:
- Speech aids are valuable tools in educational settings, enabling students with communication difficulties to participate actively in class and interact with peers and teachers.
- Versatility and Customization:
- Many speech aids offer versatile features and customization options, allowing users to tailor the device to their specific needs, preferences, and abilities.
- Integration with Technology:
- Speech aids often integrate with modern technologies, such as tablets and smartphones, making them versatile and compatible with the digital age.
- Promotion of Inclusivity:
- Speech aids contribute to a more inclusive society by providing individuals with speech challenges the tools they need to participate in various aspects of life.
- Positive Impact on Self-Esteem:
- Successful use of speech aids can positively impact an individual's self-esteem, confidence, and overall sense of well-being.
- Educational and Therapeutic Support:
- Many speech aids come with educational games, activities, and therapeutic support features that can aid in language development and communication skills.
- Environmental Control:
- Some speech aids incorporate environmental control features, allowing users to interact with and control elements in their surroundings.
Disadvantages of Speech Aid:

- Cost:
- High-quality speech aids with advanced features can be expensive, and not everyone may have easy access to these devices due to financial constraints.
- Learning Curve:
- There can be a learning curve associated with using speech aids, particularly for new users or individuals with certain cognitive challenges.
- Technical Issues:
- Like any electronic device, speech aids may experience technical issues, requiring maintenance, updates, or repairs.
- Social Stigma:
- Some users may experience social stigma or misunderstanding from others, potentially impacting their confidence and willingness to use the device in public.
- Dependency on Technology:
- Overreliance on speech aids may lead to a dependency on technology, and individuals may face challenges if the device is not readily available.
- Limited Emotional Expression:
- Some speech aids may not fully capture the emotional nuances of verbal communication, potentially limiting the expression of emotions.
- Maintenance Requirements:
- Electronic speech aids may require regular maintenance, and users need to be diligent in ensuring the device remains in good working condition.
- Not Universally Accessible:
- Speech aids may not be universally accessible due to factors like language barriers, cultural differences, or the specific needs of individuals with complex communication challenges.
It's important to note that the advantages and disadvantages can vary based on the specific type of speech aid, the individual's needs, and how effectively the device is integrated into the user's daily life. The overall impact of a speech aid depends on factors such as user training, support, and the surrounding social and cultural context.
Speech aid technology has evolved from simple communication boards to sophisticated AI-driven solutions, reshaping the lives of millions. The statistics and examples presented underscore the transformative power of these innovations, demonstrating a future where communication barriers are dismantled, and inclusivity becomes the norm. As technology continues to advance, the journey towards empowering communication for all takes a giant leap forward.



